Spam has become a momentous problem worldwide; estimates of the extent of this problem from Cisco Talos Intelligence point to 46% of the 347 billion daily emails sent in 2023 being spam. This means 160 billion spam emails are becoming part of the email ecosystem daily. This volume of spam impacts everything from productivity to employee mental health to security. Cybercriminals love email. According to PwC, in 2023, 40% of attackers used email to disrupt organizations.
Dealing with these vast volumes of malicious spam requires a dedicated mail server spam filter.
Is an anti-spam server the same as a mail server?
A mail server spam filter is a system that automatically identifies and blocks unwanted email messages, protecting users from spam and potential security threats before they reach their inbox. However, understanding the difference between anti-spam and mail servers is important to ensure you choose the best-fit solution. Conventional anti-spam servers act as mail servers augmented with email filtering software acting as a spam gateway between the mail server and the firewall. A modern and advanced anti-spam server can also be cloud-based, with the email filtering software connecting to the mail server via the MX record. This distinction affords better scalability and flexibility in a world where working environments are more complex.
Book Free Demo
Some definitions of the term anti-spam server relate to how the filtering process is conducted at the server level rather than at each device (“client”) connected to the network. Server-level filtering is much less labor-intensive than client-level filtering, giving administrators more transparent oversight of network activity. In this respect, an anti-spam server is a far more effective security solution for protecting networks against phishing, malware, and ransomware.
Do all mail servers have email filtering software?
Most mail servers already have some form of email filtering software or essential spam gateway, or at least they provide tools for administrators to set rules about how incoming emails should be managed. Some of these tools are effective and can learn to identify emails with a high probability of spam content (Bayesian Analysis) or move emails to a spam folder based on users´ previous actions (Adaptive Junk Filtering). Many productivity tools, like Outlook in Office 365 and Google Mail, include built-in anti-spam filters.
However, cybercriminals are adept at evolving new tactics that evade detection. Unfortunately, conventional in-built email filtering mechanisms are retrospective in dealing with spam, i.e., they are always playing catch-up with spammers. As such, many “default” filtering mechanisms are ineffective anti-spam servers because they fail to detect more sophisticated spam emails. Some in-built mail server spam filters do not have the fine-tuning capability of dedicated advanced anti-spam servers, which leads to significant false positive results that impact productivity and interrupt workflow.
The cost of not using an effective spam filter server
Spam email is not just a nuisance. It can lead to malware infection and financial losses from scams like Business Email Compromise (BEC). Malware in spam emails even has its own term—“malspam.”
Effective spam filter servers are essential for a modern business that may deal with thousands of such messages every month. Therefore, detection rates must be close to 100%, and false negatives and positives must be as low as possible. A single malicious spam message missed can be costly. The cost of spam to businesses worldwide is a staggering $20.5 billion every year.
Did You Know?
99.99%
SpamTitan's spam catch rate
11 Seconds
a ransomware attack occurs
$285
the average cost to manage spam per person without an email filter
56.50%
of all email is spam
The reason for the tsunami of spam is that bombardment works. Spam is successful, even if there are few successful spam deliveries. There are various studies on how much spammers earn. These studies vary, but the fact is that some types of spamming are more lucrative than others. Ransomware, for example, would see 75% of SMBs out of business within five days of an attack. Small to medium-sized companies have been found to significantly underestimate the cost of a successful ransomware attack. The cost of this cyber-attack is estimated at approximately $162,000; this includes the impact of being offline until remediation has concluded.
Regardless of which “Top 10 Cybersecurity Threats” article you read, email is the number one threat vector for businesses. Most malware attacks begin with a malicious email. Emails are also behind most phishing attacks (most of the remainder being via social media). Sophisticated attacks, like BEC, may begin with a spam email used to engineer a targeted individual socially. For example, some BEC scams start by validating a person’s email address using a blank email, a confused recipient may inadvertently reply to this email address, legitimizing further email messages from the spammer.
Book Free Demo
Many businesses implement third-party spam filter servers because of the impact of a malware infection or BEC attack and the difficulty in detecting sophisticated and complex spam. Mandy of these advanced email filter servers integrates deeply with tools like Outlook 365 to augment the capabilities of the default anti-spam filter. By adding this layer of anti-spam protection, an organization effectively turns a mail server into a spam filter server. Many third-party email filtering solutions are available on the market, but not all are equal in their capabilities.
How to identify an effective spam filter server
Fortunately, many real-world tests and reviews explore the catch rates of anti-spam filters and spam gateways. These can help evaluate solutions.
Virus Bulletin, an independent industry analyst that performs real-world tests on email security software, regularly tests spam filter servers. The latest test results show that while catch rates may have improved, this comes at a cost for legitimate emails. Many vendors have very high false negative rates. SpamTitan was the best in class, with a meager false negative rate and the highest catch rate.
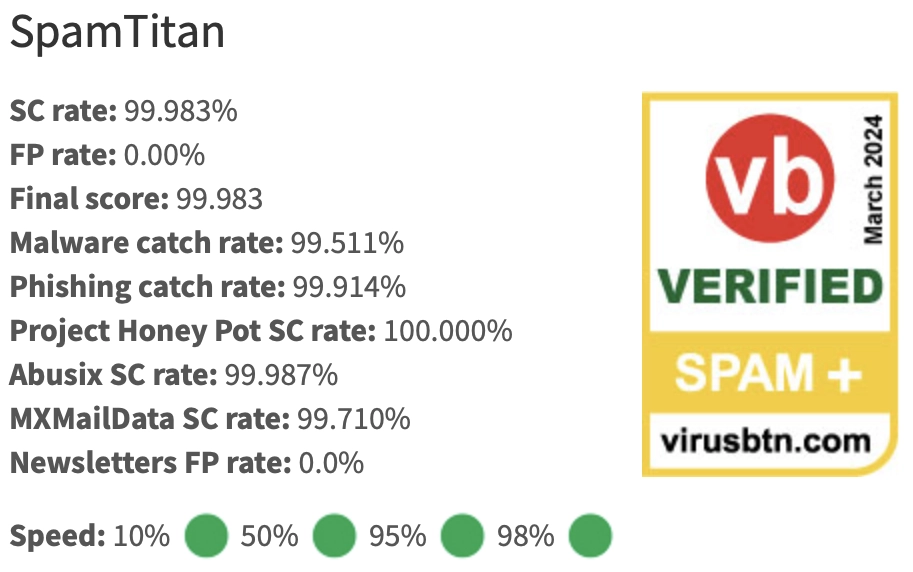
TestRadius scores:
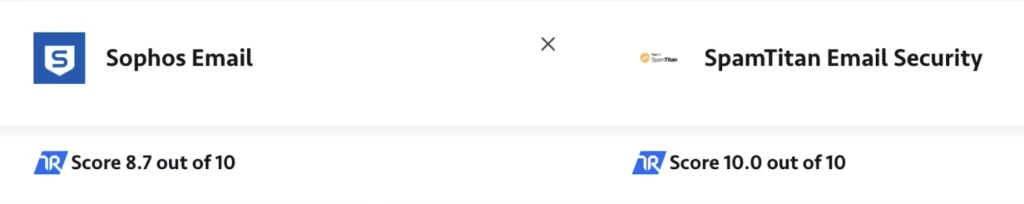
Threats from phishing, malware, and ransomware
Email-borne malicious attacks continue to be the weapon of choice for cybercriminals. Attack types show how email is weaponized and how emails are part of a more extended scam or cyber-attack. Social engineering, evasion tactics, and complex multi-part scams are some of the most common threats to a business. Spam emails are used to deliver phishing, malware, and ransomware.
Splunk’s State of Security 2024 report found that BEC scams and ransomware are still top threats to business. Generative AI is also an increasing concern, with 32% of organizations being most concerned about attackers using generative AI to create more realistic phishing emails. GenAI is also used to develop content for spoof websites. If an employee clicks a link in a spam email and is taken to one of these sites, they could be fooled into providing login credentials or other data. These credentials can then be used to gain unauthorized access to a company's app and data. Microsoft Office 365 is one of the most targeted productivity platforms. The popularity of the Microsoft suite attracts cybercriminals who create attacks based on the platform. Microsoft stated this in a recent blog, showing the extent of the problem: “Microsoft customers face more than 600 million cybercriminal and nation-state attacks every day, ranging from ransomware to phishing to identity attacks.” The Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2024 found a 2.5x increase in ransomware attacks targeting the platform.
Hear from our customers
Spam emails cost money by reducing productivity.
In addition to phishing, malware, and ransomware threats, spam emails cost businesses money by reducing productivity. Experts have estimated that a security-conscious employee takes an average of four seconds to identify and delete a spam email. Therefore, an employee receiving 12 spam emails daily would spend four minutes a week deleting spam emails—or 192 minutes per year based on a 48-week cycle.
Multiplying 192 minutes by sixty-seven employees results in 214.4 hours a year or 4.5 lost days per year just wading through and deleting spam.
Evasive tactics that test the effectiveness of a spam gateway
A conventional mail server spam filter can miss spam because of evasion tactics used by cybercriminals. Zero-day threats are a sophisticated threat type that evades traditional spam filters. A popular technique is email spoofing, where a cybercriminal constructs an email to look like it originates from a trusted source (a bank, solicitor, or business executive). If the spoofed email is sent from a not-yet-identified source of spam and is returned after greylisting, it may avoid detection by conventional email filtering software.
Spam-containing malware can also go undetected, with tactics like polymorphic malware hiding from conventional mail server spam filters. The increasing use of advanced threats like zero-day and polymorphic malware requires advanced measures.
Advanced anti-spam filter servers
Advanced anti-spam filtering servers achieve exceptional spam detection rates of more than 99.9% and identify 100% of inbound malware. The solutions can also scan outbound emails. Checking outbound emails for spam helps maintain a company's IP and brand reputation and avoids having your corporate IP address blocklisted by a global blocklist agency.
Organizations must adapt to counterbalance spam-borne cyber threats, including those built to evade conventional spam servers. Ransomware must be stopped at the entry point to ensure an attack does not steal data and shut down systems. Advanced anti-spam filter servers are designed to identify evasive phishing emails, polymorphic viruses, social engineering, and multi-part, complex spam attacks.
Social engineering manipulates users into providing data and credentials. These are then used to propagate attacks. Clever ploys that steal login credentials are enhanced by adaptive tools that evade detection, making ransomware a formidable security threat. There needs to be more than endpoint protection as evidenced by the continued threat of ransomware. An intelligent monitoring system based on advanced anti-spam filtering techniques designed for complex ransomware can detect threats in real time before they cause severe harm. Unlike traditional endpoint anti-malware, Advanced anti-spam filtering servers monitor threats in real-time to protect against active and emerging phishing URLs and zero-days. Capabilities offered by an advanced anti-spam server include the following:
Greylisting
Greylisting (sometimes spelled graylisting) is an anti-spam process that controls spam by temporarily rejecting emails from unknown sources. Using greylisting for all incoming emails from unknown IP addresses are returned to their originating mail servers with a request for the email to be resent. All SMTP-compliant mail servers will defer rejected mail and resend it after a set period (usually five minutes). As servers sending spam are rarely SMTP compliant, they may not resend the rejected mail, so the spam is blocked.
SURBL (Spam URI RBL) Filtering
When a greylisted email is returned, it undergoes a series of secondary checks. One of these checks is known as SURBL filtering. The SURBL filter layer checks URLs contained within the body of the email to ensure they do not appear on a list of URLs registered in known spam emails. This process significantly reduces the likelihood of an employee falling victim to a phishing attack.
Heuristic filter
Heuristic spam filters typically use intelligent technologies like AI algorithms to identify and predict patterns that signal spam. The system uses policies to score incoming and outgoing emails. An email will be identified as spam and blocked if it fits the score criteria. Heuristic filters are reactive to changing scenarios and phishing tactics, so they are ideal for modern evasive tactics.
Collaborative spam fingerprint checks
A vast corpus of “community intelligence” is used to build up a database of spam ‘fingerprints’ that can be fed back into the spam filter to block spam messages.
DMARC Authentication
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is an email authentication protocol that verifies that the sender of an email message is authorized to use a particular domain. It allows domain owners to protect their domains against abuse and is used by advanced anti-spam and antivirus solutions to detect and block email impersonation attacks.
Reduce exposure to spam with a SpamTitan email filter
Reducing exposure to spam is imperative to increase employee productivity and minimize phishing, malware, and ransomware threats. SpamTitan email server filters have advanced filtering mechanisms, which – subject to the acceptable spam thresholds applied by system administrators – detect 99.98% of spam emails. SpamTitan uses advanced technologies to reach this exceptional spam catch rate.
Compared with the average spam detection rate of the top ten tested spam filters, an employee previously receiving twelve spam emails daily would only receive four spam emails daily.
Dealing with twelve spam emails per day results in 214 hours per year at $17.58 average hourly rate for an office worker = $3,762 in lost time
Improved catch rates reduce the twelve spam emails down to four or fewer. Two-thirds would reduce the cost of lost productivity in dealing with spam emails to $1,254.
Also, the business would be 66% less likely to be the victim of a successful phishing attack, malware attack, BEC scam, or credential compromise.
Is SpamTitan an email gateway or cloud-based anti-spam server?
TitanHQ offers our anti-spam server with deployment options. SpamTitan is available as an anti-spam gateway server (with the additional option of clustering) or as a cloud-based anti-spam server that can be hosted in our cloud, a private cloud, or delivered by an MSP. Our solutions are easy to manage via a centralized administration portal, through which administrators can apply and adjust acceptable spam thresholds by user, group, or business-wide, with the click of a mouse.
SpamTitan is compatible with all operating systems and networks, has fully automated updating, and is scalable to unlimited mailboxes. SpamTitan also supports multiple domains, making it an ideal anti-spam server for managed service providers (MSPs) looking for a multi-tenanted solution to resell to clients. We can provide SpamTitan as a white-label product if required.
If you want to know more about how a spam email filter from SpamTitan turns your mail server into an anti-spam server, do not hesitate to contact us. Our team of experienced sales technicians will be happy to answer any questions and offer you a free trial of the SpamTitan solution that is most suitable for your requirements. It takes less than twenty minutes to turn your mail server into an anti-spam server with SpamTitan, so contact us today and start reducing your business´s exposure to spam, increasing employee productivity, and minimizing the threats from phishing, malware, and ransomware.
- Quick deployment.
- Easy synchronization with Active Directory and LDAP.
- Administered via a web-based portal. No agents are required.
- Spam Confidence Levels can be applied by the user, user group, and domain.
- Greylist, allowlist, or blocklist senders/IP addresses.
- Sandboxing
- Infinitely scalable and universally compatible.
- Available in white label format for MSPs.
Book Free Demo
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does the greylisting process work?
The Greylisting process works by returning non-whitelisted emails to their originating server. Due to the volume of emails returned to spammers’ servers (via all filtering processes), spammers’ servers often have the resubmission feature disconnected, and the spam email is never returned to the anti-spam server. This reduces the volume of spam entering the server and the workload on the server, enabling it to work more efficiently.
Is it possible to bypass the greylisting process?
It is possible to bypass the Greylisting process by allowing trusted sources so emails from trusted sources are not greylisted. It is recommended that allow listing is used with care.
While allowing a trusted sender to accelerate the delivery of their emails, the risk exists that a trusted sender´s email account could be compromised and used to send spam, malware, or phishing emails.
With high spam detection rates, what are the chances of blocking genuine emails in error?
With high spam detection rates, the chances of blocking genuine emails in error are no different than with low spam detection rates, especially if (for example) they have typically spammy subject titles (i.e., “Hello”). However, in the latest testing of SpamTitan Gateway and SpamTitan Cloud, the “false positive” rate was recorded at just 0.003%. This means only 1-in-33,333 genuine emails were mistakenly categorized as spam on optimal settings.
Most spam mail is harmless, so why implement an anti-spam server?
Although most spam is harmless, implementing an anti-spam server will prevent malicious spam from evading detection. 46% of the 347 billion daily emails sent are spam. This amounts to a significant overload on mail servers. An anti-spam filter server minimizes the amount of spam getting through, improving productivity and reducing the likelihood of a scam or cyber-attack.
How much does a better anti-spam server cost?
Advanced anti-spam server costs are priced according to the number of email inboxes you wish to protect and the time you want to subscribe to the service. The payment frequency can also be a factor. To help businesses better understand the cost of an anti-spam server, we provide an anti-spam cost calculator, or you are invited to contact us and request a quote.
What are the benefits of using an anti-spam server?
The benefits of using an anti-spam server are that it helps reduce the amount of unwanted spam received by users, improves the performance of the email system, and enhances email security by blocking potential threats such as malware, phishing, and ransomware.
Can an anti-spam server be deployed on-premises or in the cloud?
An anti-spam server can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, and hybrid environments. When an anti-spam server is deployed on-premises, it is most often maintained by the organization or a Managed Service Provider. Anti-spam servers deployed in the cloud are maintained by the software vendor, who keeps the software and spam databases up to date.
What features should I look for in an anti-spam server?
The features you should look for in an anti-spam server include robust filtering capabilities, adjustable spam detection settings, quarantine management, reporting and monitoring tools, and integration with existing email systems. You may also need to consider the server’s anti-virus capabilities and customizable policy application.
Can anti-spam servers adapt to new spam techniques?
Anti-spam servers can adapt to new spam techniques and are regularly updated with new spam signatures and detection algorithms to adapt to evolving spam techniques and maintain high accuracy in spam identification. However, users must be told to report spam emails that evade detection (rather than delete them) so evolving spam techniques can be identified quickly.
Should an anti-spam server be used in conjunction with other anti-spam measures?
An anti-spam server should be used in conjunction with other anti-spam measures to minimize the risk of mail-borne threats. Other anti-spam measures to include in a multilayered approach to combatting spam include gateway filtering, client-side spam filters, and DNS-based blocklists. Depending on the nature of your organization’s activities and employees' susceptibility to phishing, you may also want to include point-of-click URL protection in that list.

