In today’s digital age, spam emails have become a pervasive and persistent problem for individuals and businesses alike. In 2024, email spam continues to be a significant threat to productivity, security, and data privacy. Fortunately, there are many anti-spam software solutions available that can help prevent unwanted messages from cluttering up your inbox and protect you from malicious attacks.
This comprehensive guide to spam and anti-spam software tools in 2024 aims to provide a detailed overview of the latest solutions and strategies for combating spam emails. Whether you're a small business owner looking to safeguard your sensitive information, an MSP looking to improve your clients’ service or just someone who's fed up with spam, this guide has something for you. From advanced filtering techniques to email authentication protocols, we'll explore the most effective ways to prevent, detect, and eliminate spam emails using cutting-edge software tools. So, let's dive in and discover how you can protect your email and stay ahead of the spammers.
What this article will cover:
- What is spam and where does it come from?
- Spam - the stats
- Anti-spam regulations across the world
- What are spam filtering and anti-spam?
- Types of anti-spam tools and measures
- How Do anti-spam tools work?
- Why do organizations need anti-spam solutions?
- Spam and communication channels
- Anti-spam layers
- Why Office 365 / M365 spam protection isn’t enough?
- Is anti-spam the same as anti-phishing?
- How to evaluate anti-spam solutions
- Why are anti-spam tools important for organizations?
- Is an anti-spam solution worth the cost?
- Do spam filters and anti-spam solutions work?
- Typical malicious spam attacks
- Why MSPs should offer a third-party anti-spam solution?
- What are the most important anti-spam features?
- Why choose SpamTitan?
- How does SpamTitan compare?
- Anti-Spam and spam filtering frequently asked questions
What is spam and where does it come from?
Spam or email you just don't want to see in your inbox has a long history in terms of computing. The development and now insidious nature of modern spam communications are tied to the evolution of the internet. The first sighting of spam email in the wild was in 1978. ARPANET, the nascent internet, sent out an advert to 600 members of its user base. The ad was for a presentation by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) and was unsolicited and, therefore, spam. It is this unsolicited nature of communications that gave rise to the dawn of spam, and the tsunami of spam companies must deal with today. However, it wasn't until 1988 that an email chain letter was conceived with the heading "MAKE. MONEY. FAST." The full content of this spam email is kept as a digital museum piece by Rutgers. This email was the first to really make use of the viral nature of email in an unsolicited and spam-like manner.
The word 'spam' wasn't coined until a little later, in 1993. A bug in a software program caused multiple messages to be sent to a newsgroup – the term is attributed to Richard Depew, who referred to the Monty Python sketch about the meat product as' spam.'
As the internet became ubiquitous across the world, the concept of unsolicited emails sent out en masse grew. The amount of spam started to increase and proliferate. In 1994 a message headed "Green Card Lottery- Final One?" was posted to 6,000 USENET newsgroups. The ad, reportedly signed by the Phoenix law firm of Canter & Siegel, offered legal services to immigrants. The result was that thousands of USENET, angered by the waste of bandwidth and the breach of "netiquette" then inundated the law firm with emails, fax messages, and telephone. The result was that the law firm lost Internet access, and the company eventually went out of business. This collective action worked; today, spam is not so easy to stop.
In 2011, the massive "botnet" Rustock infected over a million computers with the capacity to send 30 billion emails a day. It took cooperative efforts and positive actions of industry and various governments to stop the bot.
The law firm spam ad was posted to a newsgroup. However, today, spam is communicated using any channel, including email, text and mobile app messages, social media, and phone calls. The amount of spam entering inboxes daily, for example, is simply overwhelming for individuals to stop.
Spam - the stats
Today, spam is a major worldwide problem. It causes bandwidth issues, causes email fatigue with employees, and causes legitimate emails to be lost in the overwhelming number of emails in an inbox.
In 2011, research from Statistica shows that the spam volume as a percentage of total emails was a whopping 80%. In 2022, this figure dropped to 48.6%, slightly higher than the 2021 figure of 45.6%. Radicati data suggests that 347.3 billion emails are sent daily; this amounts to around 167 billion spam emails sent across the world each day.
While there has been a decrease in spam since 2011, helped by robust measures such as the use of anti-spam solutions, however, at almost half of all emails are spam. This is still a massive amount of illegitimate and potentially malicious emails to deal with.
To manage the onslaught of daily spam emails, governments and regulators across the world have designed anti-spam regulations.
Anti-spam regulations across the world
As spam increasingly spread to inboxes the world over, regulations began to appear. International anti-spam laws set in place the restrictions needed to control and maintain privacy and consent. This effort to manage and regulate spam is one aspect of anti-spam measures. Some of the countries that enforce anti-spam laws include the following:
USA – 2003 CAN-SPAM Act
Canada – CASL
Australia – Spam Act of 2003
European Union – Directive on Privacy and Electronic Communications
UK – Data Protection Act
Germany – Federal Data Protection Act, Telemedia Act, Act Against Unfair Competition
France – Article L. 43-5 Code of Postal and Electronic Communications
Israel - Communications Law (Telecommunications and Broadcasting), 1982 (Amendment 2008)
South Africa - Consumer Protection Act, 2008
United Kingdom - Privacy and Electronic Communications (EC Directive) Regulations 2003
Singapore - Spam Control Act 2007
What are Spam Filtering and Anti-Spam?
Spam filtering is a process of identifying and blocking unsolicited or unwanted messages, also known as "spam," from entering an email inbox. Spam filters work by analyzing various characteristics of incoming messages, such as the sender's email address, message content, and attachments to determine whether the message is likely to be legitimate or not. Depending on the level of filtering set by the user or organization, spam filters can automatically move suspicious messages to a separate folder (quarantine), mark them as spam, or even delete them outright.
Anti-spam, on the other hand, refers to a broader range of techniques and strategies for preventing and combating spam. In addition to spam filtering, anti-spam measures may include tactics such as email authentication protocols, blocklists and whitelists, content-based filtering, and user education and awareness. The goal of anti-spam is not only to filter out unwanted messages but also to reduce the overall amount of spam that is sent and to minimize the impact of spam on email users and systems. Ultimately, anti-spam is a multi-layered approach that aims to prevent, detect, and mitigate the effects of spam emails.
Types of anti-spam tools and measures
Anti-spam tools are software applications or services designed to prevent or mitigate the impact of spam emails. They work by analyzing incoming messages and applying various filters and rules to identify and block unsolicited or unwanted emails.
There are several types of anti-spam tools and strategies available, including:
- Spam filters - software programs that use a combination of algorithms and rules to determine whether a message is likely to be spam or legitimate. They may also use heuristics and machine learning to adapt to new forms of spam.
- Email authentication protocols - methods for verifying the identity of the sender and ensuring that the message has not been tampered with or spoofed. Popular authentication protocols include SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Blocklists and whitelists - lists of IP addresses or domains that are known to be either sources of spam (blocklists) or trusted senders (whitelists). Anti-spam tools may use these lists to block or allow incoming messages.
- Content-based filtering - techniques that analyze the content of a message to identify spam keywords, phrases, or patterns. Content-based filters may also block messages that contain malicious links or attachments.
- Security awareness training programs - user education and awareness and educational resources that help users recognize and avoid spam emails.
- Phishing simulations – specialized platforms that can be configured to send out fake spam and phishing messages to employees to train them how to spot a spam email.
How Do Anti-Spam Tools Work?
Modern anti-spam solutions use a multi-layered approach to detect spam. The mechanisms included in the multi-layered approach vary according to each email service or software provider, but generally consist of a Real-time Blackhole List, Recipient Verification Protocol, Sender Policy Framework and a content analysis tool. The functions of each mechanism are described below:
Real-time Blackhole Lists
Real-time Blackhole Lists (RBLs) are a type of anti-spam tool that maintains a list of IP addresses that have been identified as sources of spam or other forms of abusive behavior. RBLs work by providing a real-time lookup service that allows email servers and other anti-spam tools to check whether an incoming email has originated from a blocklisted IP address.
When an email server receives an incoming message, it can query one or more RBLs to determine whether the message has been sent from a blocklisted IP address. If the IP address is found on one or more RBLs, the email server may choose to block or quarantine the email or assign it a higher spam score.
RBLs are maintained by a variety of organizations, including ISPs, anti-spam vendors, and non-profit groups. These organizations typically use a combination of automated tools and manual review to identify IP addresses that are likely to be sources of spam. Some RBLs may also include IP addresses that have been associated with other forms of abusive behavior, such as malware distribution or phishing.
While RBLs can be an effective tool for blocking spam, they are not without their drawbacks. One potential issue is the risk of false positives, where legitimate emails are incorrectly flagged as spam and blocked. Additionally, some critics argue that the use of RBLs can create a centralized system of control over email delivery, which may have implications for freedom of speech and privacy. As with any anti-spam tool, the use of RBLs should be balanced against the need to ensure that legitimate emails are not unfairly blocked.
Recipient Verification Protocol
Recipient Verification Protocol (RVP) is a technique used by some anti-spam tools to verify the existence of email addresses before accepting incoming messages. RVP works by sending a probe email to the recipient's email address to verify that it is valid and active. If the email address is invalid or inactive, the anti-spam tool may reject the incoming message or assign it a higher spam score.
There are several ways in which RVP can be implemented. One approach is to use Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) commands to check whether the recipient's email server will accept the probe email. Another approach is to use a web-based interface to query the recipient's email server directly.
RVP can be an effective tool for reducing the impact of spam emails, as it allows anti-spam tools to verify that an email address is valid before accepting incoming messages. This can help to reduce the number of undeliverable emails and prevent email servers from being overwhelmed by spam traffic.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to RVP. One concern is that it can create additional overhead for email servers, as they may need to process many probe emails. Additionally, some legitimate emails may be incorrectly rejected if the recipient's email server is configured to block incoming messages from unknown senders.
Sender Policy Framework
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication protocol that is designed to prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks. SPF works by allowing email servers to check whether an incoming message is sent from a legitimate source by verifying the sender's domain name against a list of authorized IP addresses.
When an email is sent, the sending server adds an SPF record to the message's DNS information. This SPF record lists the authorized IP addresses that are allowed to send email on behalf of the sender's domain. When the receiving server receives an email, it checks the SPF record against the IP address from which the email was sent. If the IP address is not listed in the SPF record, the email may be rejected or assigned a higher spam score.
SPF can be an effective tool for preventing email spoofing, as it verifies that the sender's IP address is authorized to send email on behalf of the domain. This can help to prevent phishing attacks, where attackers attempt to impersonate a legitimate sender to trick recipients into divulging sensitive information.
However, there are some potential limitations to SPF. One issue is that it relies on the recipient's email server to check the SPF record, and not all email servers support SPF. Additionally, SPF does not protect against other types of email fraud, such as spear phishing, where attackers target specific individuals rather than sending mass emails.
Content Analysis Tool
A Content Analysis Tool is an anti-spam tool that analyzes the content of incoming emails to determine whether they are likely to be spam. Content Analysis Tools use a combination of heuristics, rules-based analysis, and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns in email content that are commonly associated with spam or other types of unwanted messages.
Some of the key features of Content Analysis Tools include the ability to scan email content for keywords, analyze message headers and metadata, and examine the structure and formatting of email messages. Content Analysis Tools may also be configured to check for other indicators of spam, such as the use of suspicious URLs, attachment types, or email addresses.
When an email is flagged as spam by a Content Analysis Tool, it may be rejected or quarantined by the recipient's email server or assigned a higher spam score. Content Analysis Tools may also be configured to allow administrators to set custom rules and filters to block or allow specific types of email based on content or sender information.
Content Analysis Tools can be an effective tool for reducing the impact of spam emails, as they allow anti-spam tools to identify and block messages based on their content rather than relying solely on sender information. However, there is also a risk of false positives, where legitimate emails are incorrectly flagged as spam and blocked. To minimize this risk, Content Analysis Tools should be configured with appropriate sensitivity settings and regularly updated to ensure that they are accurately identifying new types of spam messages.
Reputation scoring
One significant development from the mid-1990s is that Real-time Blackhole Lists are now more refined than they were. This is due to RBL agencies assigning an “IP Reputation Score” to IP addresses based on factors such as email open rates, click-through rates, spam complaints, and hard bounces (emails returned to their senders because the domain name does not exist or the recipient is unknown).
Modern anti-spam solutions consider IP reputation scores along with the ratings calculated by Content Analysis Tools to assign a “spam score”. System administrators can set a “Spam Acceptance Threshold” and, if the spam score exceeds the threshold, the email is rejected, quarantined, or flagged, depending on how the business’s spam filter has been configured.
Why do organizations need anti-spam solutions?
Spam is many things. Spam is a nuisance at best; at worst, it can be a delivery mechanism for malware or a mechanism to deliver phishing campaigns. Spam has a wide-reaching negative impact on organizations, with examples including:
Decreased productivity
Spam is the cause of decreased productivity. According to McKinsey, employees spend around 28% of their day dealing with emails. This is exacerbated by the number of emails in the average employee’s inbox, which is 200. Just deleting an email takes around 3 seconds. The overhead caused by removing unwanted emails has a direct impact on productivity.
Another related benefit is that legitimate emails can get lost in the many unwanted spam emails that enter an inbox. Having to manually remove spam emails every day can also potentially result in the removal of an important business email. Therefore, anti-spam measures that reduce the number of emails a person must wade through is beneficial.
Malicious emails
Spam is often associated with annoying rather than malicious emails. However, scammers may use spam to obfuscate their malicious intentions. Spam is often sent out using bots to mass mail indiscriminate emails. These may not be targeted in the way that spear phishing emails are, but these mass mailer spam emails can still be a danger. Malicious spam uses typical scam and phishing tactics to manipulate employees and other individuals.
For example, a spam message sent en masse may contain phishing links to a spoof anti-virus page to ‘update’ a well-known anti-virus software. Chances are that some of the recipients of this malicious spam will have that anti-virus installed and will fall for the trick. A single click on a malicious link or website could result in malware infection.
Another typical malicious spam attack is the money spammer. Crypto-scams often begin life as spam messages. Crypto-based investments are often sent out via mass mailing to trick people into investing in fake crypto schemes. The spam email may also link to a spoof website that offers initial coin offerings (ICOs) and requires a deposit of cryptocurrency into a compromised wallet.
Psychology of spam and scam
Cybercriminals rely on being able to manipulate employee behavior to execute a phishing campaign. If employees are inundated with emails, many of which are spam, it can cause email fatigue. This can be exploited by cybercriminals, and tired employees clicking on links without thinking.
Also, cybercriminals may use spam as a reconnaissance to check if an email address is live. If the employee opens the spam email, this alerts the cybercriminals that this is an active account and may be targeted for phishing or malware infection.
Anti-spam solutions are used to prevent spam from being a nuisance, reduce productivity, steal data, or infect your organization with malware.
Compliance with regulations
Anti-spam regulations and data protection laws exist across many countries worldwide. These regulations expect that companies apply protective measures to secure data and protect privacy. Anti-spam solutions help organizations to meet anti-spam compliance requirements and data protection laws by reducing the risk of data breaches from phishing attacks or malware infections.
Reputation protection
Spam can result in malware infection, and some malware can steal employee email credentials. Once the account is in the hands of the spammer, it will be used to send spam from your business webmail server. The result will be a harmed reputation and potentially your own domain being placed on spam blocklists. This can damage your company's reputation and brand image.
Spam and communication channels
In the early days of spam, spammers used message boards on forums to get their spam messages out. As email became increasingly used, especially by businesses, the spammers turned to email messaging to deliver spam.
Spammers use various methods to collect email addresses for spam purposes, including the following.
Harvesting bots: bots crawl the internet and harvest email addresses. Marketers generate harvested email address lists and are often sold on as a contact list.
Dark web marketplaces: hackers only need to go to a dark web marketplace or WhatsApp hacker chat room to hire or buy massive numbers of stolen email addresses.
Dictionary attacks: This is a method where spammers will auto-generate thousands, often hundreds of thousands, of potential email addresses using the same domain. The computer program generates a possible likely email using the target domain suffix, e.g., adam@targetdomain.com; these email addresses are then used to attempt to deliver spam.
Sending spam mail
Marketers that are spammers will use their marketing company website to send out messages until spambots stop them.
Malicious spammers either hijack a web server or use their web server, paying for the service using a stolen credit card. Sometimes, spammers will infect devices with bots that send out messages on their behalf. Trickbooster, a variant of Trickbot, infected the desktops and laptops of individuals before using their accounts to send out spam emails, then removing the emails from sent items to avoid detection.
Today, spammers use any channel to get their spam messages out, including text messages and mobile apps. In recent years, social media has become a spammers' paradise. Spam on social media is not just contained in the original post. Spammers often use comments under posts to link to malicious websites or promote scams. A 2023 report by Orbit Media, into the most spammy social media platforms found that Facebook (25%) and Instagram (20%) were the spammiest, with TikTok not far behind at 17%.
Like all types of cyber threats, fraudsters, and spammers will use whichever mechanism is widespread and likely to succeed. This is why it is essential to use a multi-layered anti-spam approach.
Anti-spam layers
Layers of conventional and advanced anti-spam measures are needed to stop modern, complex, and evasive spam.
Manual preventative anti-spam techniques
As an individual, there are ways to help prevent your email address from being abused by spammers. Spammers and scammers both use email list harvesting to send out mass mailings. Be careful with whom and where you share your email address. For example, don’t post your email address on social media posts or sites, do your homework before signing up for online accounts, and take care of other email addresses by placing email addresses in the BCC field when sending emails to multiple people.
Email address obfuscation is another method that can be used to hide email addresses from harvesting. Spambots trawl websites looking for email addresses to spam. Email Address Obfuscation provides a method to hide email addresses on a web page from spambots while making them visible to humans.
Conventional spam gateways
Spam filtering began by using blocking methods to stop spam. Conventional spam filters were the first to use blocklists. One of the most well-known blocklist vendors is Spamhaus, who came on the anti-spam scene in 1998. Spamhaus provides DNS-based Blocklists (DNSBLs) and offers other anti-spam and anti-phishing intelligence. Blocklists, however, must keep up to date with fast-changing spam domains. This makes blocklists more of a retroactive method. Instead, spam filters and gateways have been updated to take a more proactive approach, applying multiple layers of catch-all filters to stop modern spam from entering a corporate network.
Advanced anti-spam gateways
Just as spam has evolved, so too have anti-spam filters kept up with technological changes. Today, advanced anti-spam filters use layers of technology that are increasingly sophisticated to filter out all types of spam. Advanced spam filters are multi-layered, applying rules and policies that are augmented by verification, authentication, and intelligent technologies such as machine learning. The following technology layers are typically found in advanced anti-spam solutions:
Conventional filter layers
- Real-Time Blocklists (RBLs) and graylists: set a baseline to identify and block spam from recognized spam-supporting ISPs.
- Harvesting/dictionary attack protection: filters identify unauthorized words or content in an email, then block or quarantine the email if these words are found.
- Allowlists (safe listing): A global allow list page of allowed words and content is used to always allow authorized messages.
Advanced layers
- Bayesian Analysis: based on a self-learning system that continuously improves as it learns.
- Auto Learning: AI and machine learning are used to protect against spam threats by using pattern detection in real-time.
- Heuristics: detects viruses present in spam messages by examining code for suspicious properties.
Did You Know?
99.99%
SpamTitan's spam catch rate
11 Seconds
a ransomware attack occurs
$285
the average cost to manage spam per person without an email filter
56.50%
of all email is spam
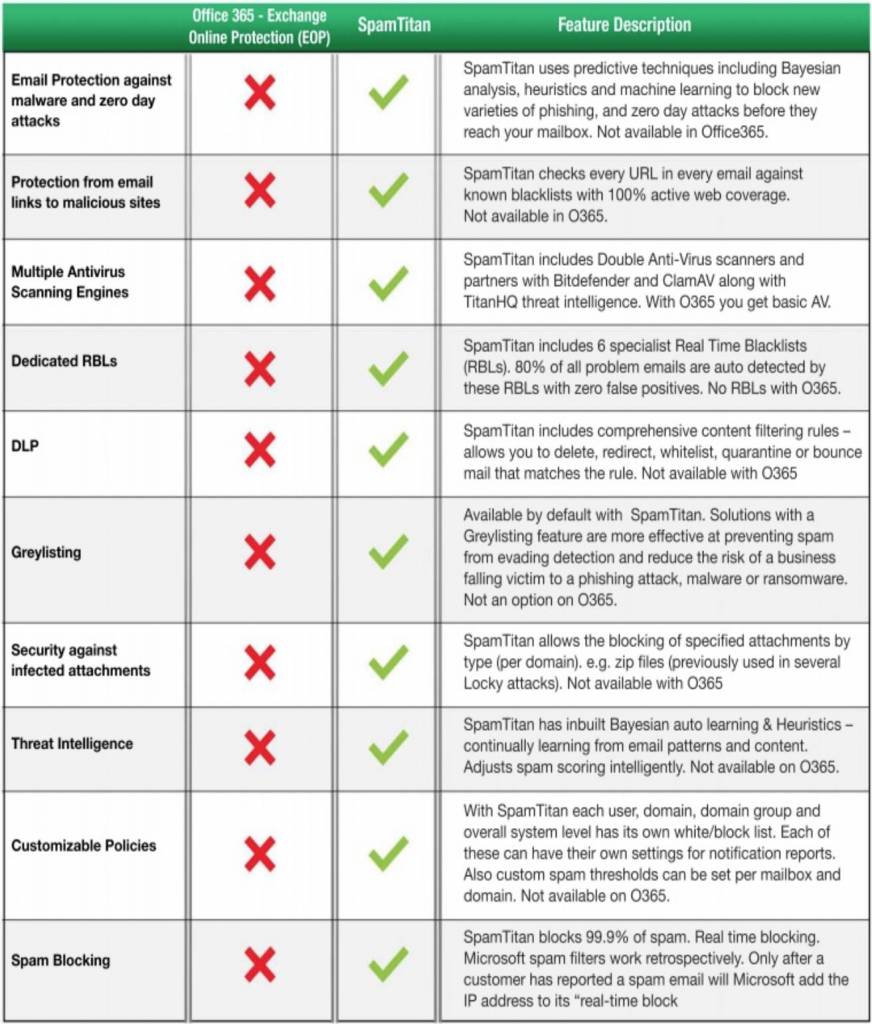
Why Isn’t Office 365 / M365 Email Anti-Spam Enough?
While Microsoft 365 (previously known as Office 365) includes built-in spam protection features, it may not be enough for organizations that require more advanced or customizable anti-spam solutions. Microsoft 365 security tool is known as “Exchange Online Protection (EOP).” EOP is used by security admin to configure and enforce policies and filters to detect and protect against phishing and spam. EOP comes with Microsoft 365 Defender and is also part of Exchange Online or as a standalone service.
One limitation of M365's built-in spam protection is that it may not be able to identify all types of spam or phishing attacks. Zero-day detection is an example of a limitation in EOP, protection being retrospective rather than predictive. This can be particularly problematic for organizations that are frequently targeted by sophisticated phishing attacks, which may be designed to evade basic spam filters.
Another limitation is that it may not provide the level of customization that some organizations require. For example, some organizations may need to set up custom filters and rules to block emails based on specific keywords or sender information, which may not be possible with M365's built-in spam protection. This limitation can potentially leave an organization open to social engineering attacks, which are intrinsic to many spam emails.
M365's spam protection may not provide the same level of reporting and analysis as dedicated anti-spam solutions. Organizations that need to closely monitor their email traffic or track the effectiveness of their anti-spam measures may require more advanced reporting and analysis tools than are available with M365.
Overall, M365's built-in spam protection can be effective for many organizations and can be used alongside more powerful multi-layered anti-spam solutions. However, EOP used alone or as a primary protection layer, may not be enough for organizations with more complex or demanding anti-spam requirements. In these cases, dedicated anti-spam tools may be necessary to provide the level of protection and customization that is needed.
Is anti-spam the same as anti-phishing?
Spam and phishing are two sides of a coin that uses social engineering to trick people into doing something like revealing personal information or clicking a link.
Spam is typically sent for commercial, usually marketing, purposes but is unsolicited. However, spam can also be used as a device to send malicious elements to attempt to harvest personal data or gain unauthorized access to a device.
As such, there is some fuzziness around the question, "Is spam the same as phishing?"
Phishing, however, is only malicious. Phishing campaigns are dedicated to manipulating people into handing over sensitive or personal data, providing login credentials, or inadvertently installing malware.
Both spam and phishing use social engineering to manipulate user behavior. If a spam or phishing message lands in an inbox, it can be difficult for people to detect. This is where security awareness training as a layer of email security and anti-spam measures comes into play. Security awareness training gives people the knowledge to recognize the tricks used during social engineering.
How to evaluate anti-spam solutions
Choosing which anti-spam solution to use can be difficult as there are lots of options. However, certain technologies and features are an essential part of an advanced multi-layered approach to tackling spam. Here are some of the features and functions to ask about when evaluating an effective anti-spam solution:
Is the anti-spam solution cloud-based?
Cloud-based anti-spam filters stop spam from entering your corporate network. Cloud anti-spam services are hosted in the cloud as opposed to a physical appliance or on-premises software installation. Cloud-based anti-spam solutions run as a software-as-a-service (SaaS), making the spam filtering service on-demand and highly scalable. Cloud-based email filters provide a centralized console where companies can control the policies and rules needed to optimize their anti-spam instance. Unlike appliances and software installations, a cloud-based anti-spam setup is quick and easy, with a simple change to an MX record.
Does the anti-spam solution provide Real-Time Protection?
Threats are continually updated by spammers and scammers. The best way to deal with emerging and changing spam threats is to have multiple layers of advanced and intelligent threat detection. The use of specialist Real-Time Blocklists (RBLs) keeps malicious domains current to ensure that spam is rejected or quarantined.
Does the solution use machine learning?
Spam detection is complicated as it can be difficult to determine what is spam and what is not. Machine learning is used to predict spam by comparing sequences of words in emails. The machine learning algorithm is trained using multiple millions of emails. Combining machine learning and behavioral analysis provides enhanced capabilities for complex problems such as spam detection. AI and machine learning techniques help to identify zero-day phishing attacks.
Does the solution support greylisting?
Greylisting blocks all inbound emails to sweep for any malicious or spam content. If the mail is legitimate, the sending server will be instructed to re-send, and the mail will be accepted. This is done at lightning speed.
Can the anti-spam solution be centrally controlled?
Cloud-based anti-spam solutions provide a web-based portal where administrators can carry out essential maintenance and controls: this includes whitelisting approved senders, applying "acceptable spam thresholds," monitoring real-time activity on the mail server and scheduling activity and quarantine reports.
What about reporting and analytics?
Anti-spam solutions must offer extensive reporting capability based on email analytics. Reports should be available both on-demand or scheduled, providing an at-a-glance view of various metrics associated with spam and phishing detection and prevention. These reports are useful for demonstrating compliance with data protection and anti-spam laws.
Does the anti-spam filter offer Sandboxing?
Sandboxing provides an isolated test environment on a network to inspect incoming suspicious files or code. This ensures that dangerous emails do not cause damage to the host system or network.
Are anti-spam policies configurable?
Each business will have its own requirements and anti-spam policies. An email filtering service should provide the facility to handle granular policy generation and enforcement. Policies should be applicable on an individual user, user-group, or business-wide basis through integration with directory services such as AD.
What about checking for outbound spam?
Outbound scanning is an important feature to prevent damage to a company's reputation. Outbound scanning capabilities are used to identify unauthorized emails, including spam, malware, and phishing attacks, that have come from inside the company. These unauthorized emails may be sent by malicious insiders or via compromised mailboxes.
Why are Anti-Spam Tools Important for Organizations?
Organizations should use an anti-spam solution for several key reasons, including:
- Protection against phishing and malware: Anti-spam tools can help protect an organization from phishing attacks, which are designed to trick users into divulging sensitive information, as well as from malware that can be delivered through email attachments or links.
- Improved productivity: Spam emails can be a significant drain on employee productivity, as they can take time to sort through and delete. By using an anti-spam tool, organizations can reduce the amount of spam that employees receive, allowing them to focus on more important tasks.
- Cost savings: Spam emails can also have a financial impact on organizations, as they can consume storage space and network bandwidth, and potentially lead to costly security breaches. By reducing the volume of spam emails, organizations can save on these costs.
- Regulatory compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that require them to protect sensitive data, such as personal information or financial data. Anti-spam tools can help organizations meet these compliance requirements by reducing the risk of data breaches resulting from phishing attacks or malware infections.
- Customizable filtering: Anti-spam tools often allow organizations to customize their filtering rules and policies, allowing them to block specific types of emails or set up filters based on sender information or keywords. This can help organizations better manage their email traffic and reduce the risk of unwanted or malicious emails.
Is an anti-spam solution worth the cost?
Not using a spam filtering solution may result in stolen data, lost login credentials, ransomware infection, and lost productivity. Factors such as the cost of a data breach, which according to IBM, is $3.31 million for companies with fewer than 500 employees and $3.29 million for companies with 500–1,000 employees. These costs put the cost of anti-spam protection into perspective; the ROI (return on investment) analysis of buying an anti-spam filtering solution should factor these risks and costs into the equation.
Read more on the ROI when using SpamTitan.
Spam filters vary in price; alternatively, free spam filter options are available. However, the free spam filters are usually basic and can mix up spam and legitimate emails - hence why you may end up looking for business emails in your spam folder. Businesses that have multiple computers and employees are best served by a paid-for spam filter. However, while the cost of an anti-spam filter ranges in price, some advanced anti-spam gateways start at less than $1 per user. The option to use an MSP to deploy and manage a spam filtering solution on behalf of a company is also a good cost-effective option. MSPs have buying power and usually get good deals for their clients.
Do spam filters and anti-spam solutions work?
SpamTitan is 99.9% effective at stopping spam from entering your employees’ inboxes. But not all spam filtering solutions are as effective. Businesses are inundated by spam. Spam emails only ever get more sophisticated, and spammers use tactics to evade detection by conventional anti-spam software. The most effective way to stop these modern spammers is to use multiple layers of spam filters that include the sophistication of AI and machine learning. These increasing layers of protection will capture almost all the possible current and emerging threats and even predict zero-days. Spam filters do work, but only if they are designed to use finer and more granular filters to capture all threats.
Can an MSP deliver the anti-spam solution?
Some anti-spam filters can be deployed and managed by a managed service provider (MSP). These solutions are multi-tenant and can be white-labeled to allow an MSP to add their own branding. Anti-spam solutions designed for delivery by an MSP should provide a full suite of APIs to incorporate the solution into back-office management systems. Other features must include:
- No end-user software installations.
- No bandwidth-per-client limits.
- Multiple clients can be managed from the same portal.
- A choice of hosting options exist – our cloud, a private cloud, or within your own cloud.
Typical malicious spam attacks
There are many malicious spam types, but here are some of the latest examples to give you a view of the type of messaging and tricks that spammers use:
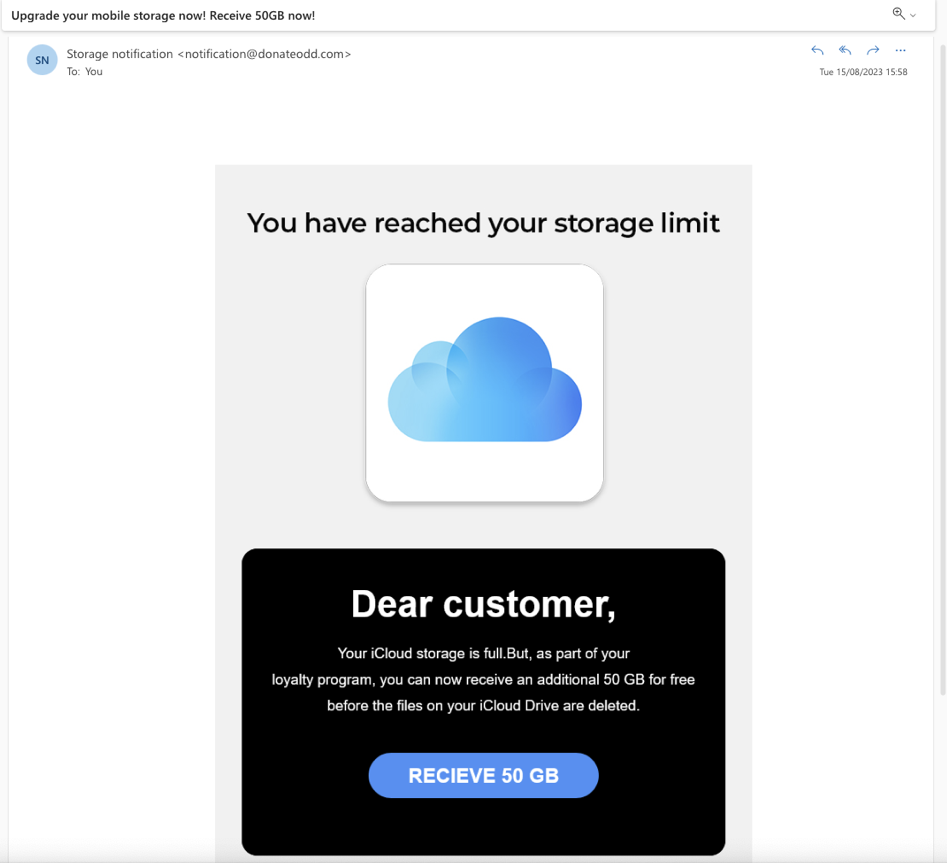
“You’ve reached your limit!”
Most of us use cloud storage for photos and other files. The “You’ve reached your storage limit” spam looks just like an email from Apple iCloud. However, this email contains a malicious link. The email is designed to socially engineer the recipient, playing on concerns about losing precious photos and offering an incentive to click the link.
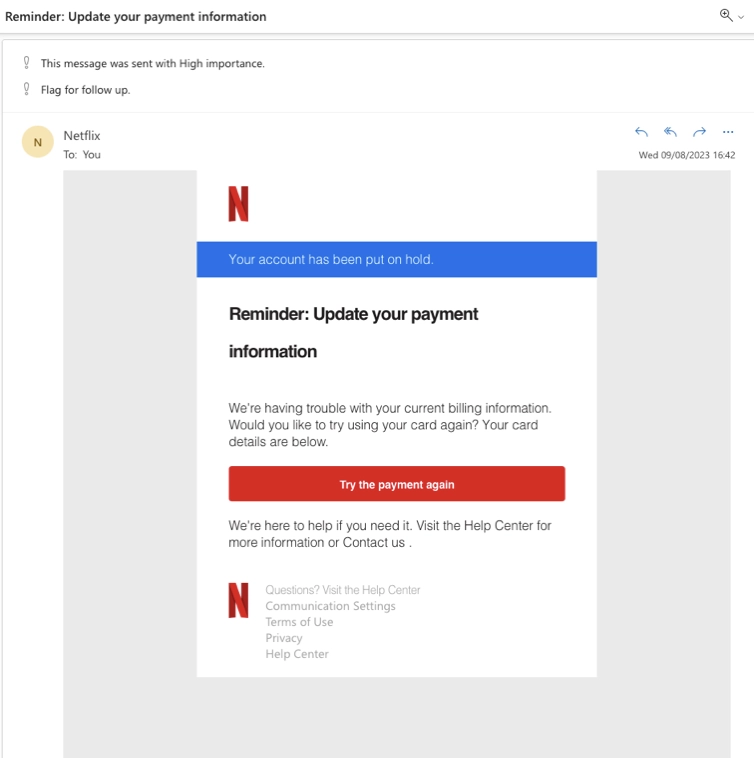
“Update your payment information.”
Well-known brands are often spoofed in malicious spam emails. In this case, Netflix was the spoofed brand. This spam attack relied on concern by the recipient about losing access to their Netflix account. The email contains a link that will attempt to steal credit card details.
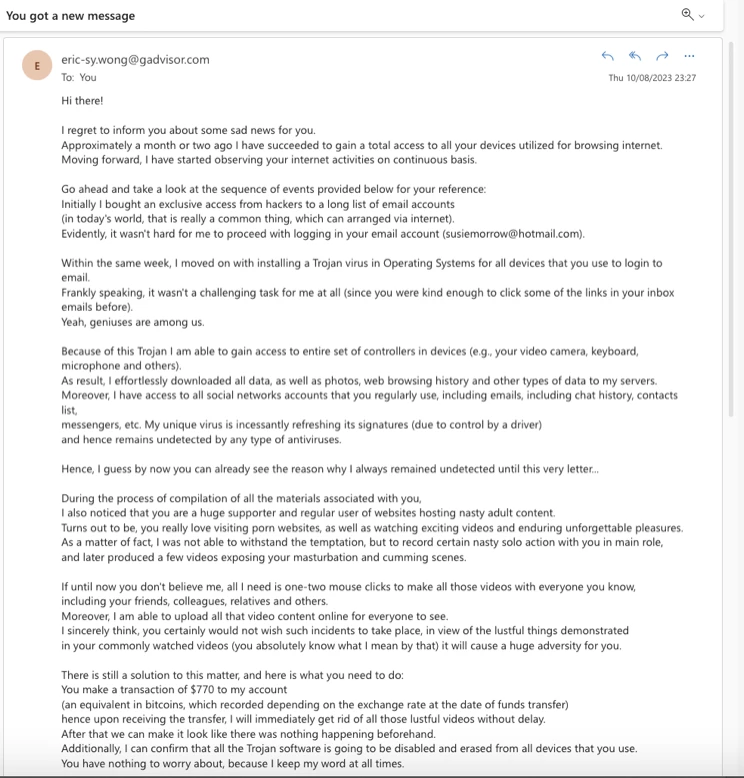
“I’ve got access to your devices.”
Malicious spam may attempt to extort money using fear, concern, and doubt. In this example, the spammer created a lengthy email explaining that they had hacked into the device, and to prevent embarrassment and shame, you must pay $700 worth of bitcoin to the spammer. The spam email provides a Bitcoin wallet address to send the cryptocurrency to.
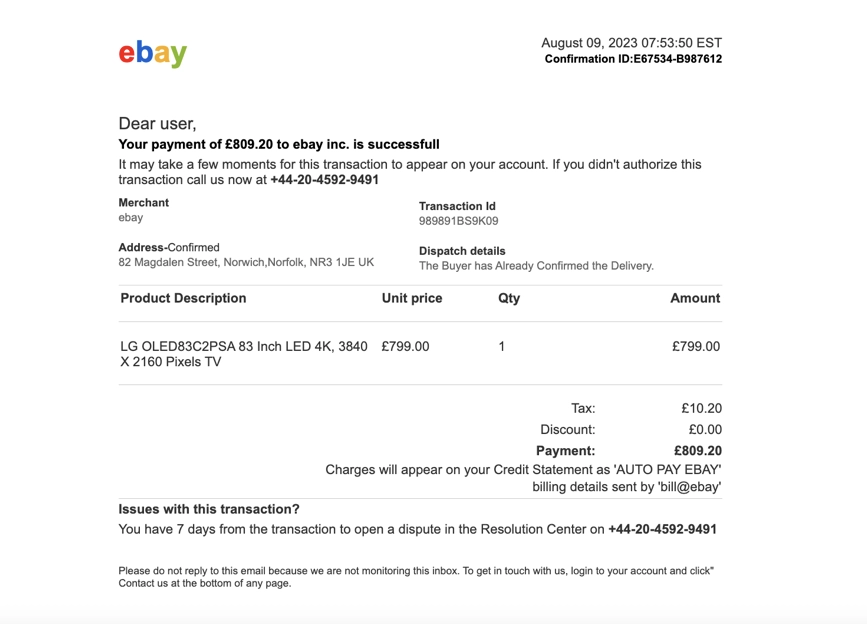
“Confirmation of purchase”
Variations on this theme are commonly found in spam emails. This email uses eBay branding and uses social engineering to make the recipient feel concerned about a purchase that they would not have made. No links: instead the email urges the target to make a call to stop the purchase -the call will go through to a scammer who will attempt to extract personal details.
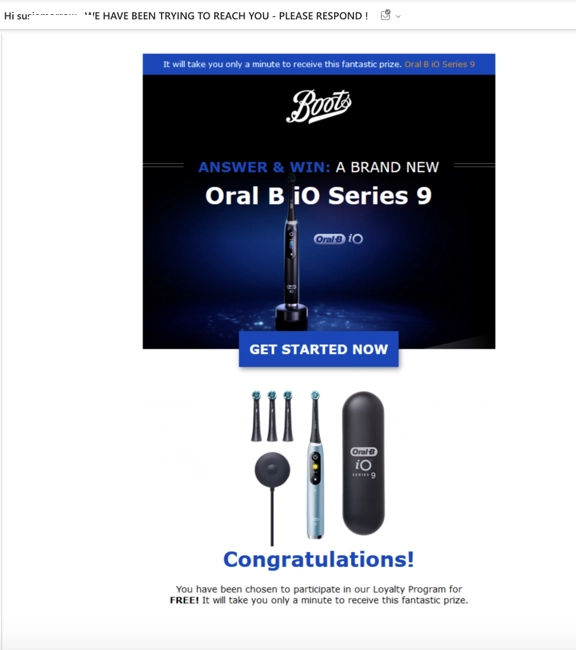
“Please respond, free gift!”
Urgency is a common theme in malicious spam. This email tempts the recipient by offering a free gift. To claim the gift, you must click the link and enter your details – of course, these details will be sent straight to the spammer.
Hear from our customers
Why MSPs should offer a third party Anti-spam solution
Managed Service Providers (MSPs) can garner many benefits from offering a third-party anti-spam solution to their clients, including:
Improved security: Offering a third-party anti-spam solution can help MSPs improve the security of their clients' email systems. Dedicated anti-spam solutions often offer more advanced and customizable filtering than built-in solutions, which can help reduce the risk of phishing attacks, malware infections, and other email-based threats.
Additional revenue stream: A third-party anti-spam solution can also provide MSPs with an additional source of revenue. By reselling anti-spam solutions to clients, MSPs can generate ongoing subscription revenue, as well as potentially offering additional services related to the implementation and management of the solution.
Competitive differentiation: Advanced email protection solutions can help MSPs differentiate themselves from competitors who only offer basic built-in anti-spam features. By offering more advanced anti-spam solutions, MSPs can position themselves as more capable and proactive in addressing their clients' security needs.
Client satisfaction: Providing clients with a robust and effective anti-spam solution can help improve client satisfaction and retention. By helping clients reduce the risk of email-based threats and improve their email productivity, MSPs can build stronger relationships with clients and reduce the risk of churn.
Compliance requirements: Many industries are subject to regulations that require them to protect sensitive data, including email communications. By offering a third-party anti-spam solution, MSPs can help clients meet these compliance requirements and avoid potential penalties or legal issues.
Overall, offering a third-party anti-spam solution can provide MSPs with a range of benefits, including improved security, additional revenue, competitive differentiation, client satisfaction, and compliance support.
What are the most crucial Anti-Spam features?
The most important anti-spam features vary depending on the needs of the organization, but some of the key features to look for include:
- Advanced filtering: An effective anti-spam solution should have advanced filtering capabilities that can detect and block spam emails with a high degree of accuracy. This may include keyword-based filters, sender reputation checks, and machine learning algorithms that can adapt to new threats over time.
- Content analysis: A content analysis tool can analyze the contents of incoming emails to detect spam messages, phishing attempts, and other malicious content. This may include scanning for specific keywords, attachments, or URLs that are commonly associated with spam or malware.
- Real-time updates: Anti-spam solutions should be updated in real-time to ensure that they are able to detect and block new threats as they emerge. This may include receiving updates from threat intelligence feeds or machine learning algorithms that can learn from new threats in real-time.
- Customizable policies: Organizations should be able to customize their anti-spam policies to meet their specific needs. This may include setting up filters based on sender information, keywords, or other criteria, as well as blocking specific types of email attachments or messages.
- Recipient verification: A recipient verification protocol can help reduce the risk of spam messages being delivered to invalid email addresses by checking the validity of the recipient's email address before delivering the message.
- Reporting and analytics: An effective anti-spam solution should provide reporting and analytics tools that allow administrators to monitor and analyze incoming email traffic. This can help identify trends and patterns in spam and malware attacks, as well as identify potential vulnerabilities in the organization's email security.
Why choose SpamTitan?
There are several great reasons why users may choose SpamTitan over other similar tools for email anti-spam, including:
Accuracy: SpamTitan has a reputation for being highly accurate in detecting and blocking spam emails, thanks to its advanced filtering capabilities and machine learning algorithms. Block rate for SpamTitan is 99.9% of spam emails. SpamTitan reduces the risk of false positives and ensure that legitimate emails are delivered promptly.
Customizability: SpamTitan offers a range of customizable policies and filters that allow organizations to tailor their anti-spam protection to their specific needs. This can help improve the accuracy of the filtering and reduce the risk of spam emails slipping through.
User-friendly interface: SpamTitan has a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and use, even for non-technical users. This can help reduce the learning curve and ensure that the anti-spam solution is adopted more quickly and effectively.
Scalability: SpamTitan is designed to be scalable, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes. This means that it can grow with the organization as its needs change, without requiring a major overhaul of the anti-spam solution.
Value for money: SpamTitan offers a competitive pricing model that provides good value for money, especially for small to medium-sized businesses. This can make it an attractive choice for organizations that are looking for effective anti-spam protection without breaking the bank.
Support: SpamTitan offers comprehensive support services that include technical support, training, and documentation. This can help organizations get up and running with the anti-spam solution more quickly and easily and ensure that any issues are resolved promptly.
Overall, users may choose SpamTitan over other similar tools for email anti-spam because of its accuracy, customizability, user-friendly interface, scalability, value for money, and support services.
How does SpamTitan compare?
Let’s compare SpamTitan to other email spam protection tools in the market:
Barracuda
Barracuda is a well-established anti-spam tool that provides email protection solutions for businesses. The Barracuda Email Security Gateway is one of its popular products that is designed to protect businesses against email-borne threats such as spam, viruses, and phishing attacks. It uses advanced filtering techniques such as content analysis, sender reputation checks, and machine learning algorithms to detect and block spam emails before they reach the user's inbox. The tool is regularly updated with the latest threat intelligence and can also provide real-time protection against emerging threats. With a range of customizable policies and filters, the Barracuda Email Security Gateway can be tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses of all sizes.
Compared to SpamTitan:
- Filtering techniques: Both tools use advanced filtering techniques such as content analysis, sender reputation checks, and machine learning algorithms to detect and block spam emails.
- User interface: SpamTitan has a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and use, while Barracuda's interface may require some technical expertise to operate effectively.
- Pricing: SpamTitan's pricing model is generally considered more affordable and flexible, especially for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Support: SpamTitan offers comprehensive support services that include technical support, training, and documentation, while Barracuda's support may be more limited.
Ultimately, the choice between SpamTitan and Barracuda will depend on the specific needs and preferences of the organization, as both tools offer robust anti-spam features that can effectively protect against email-borne threats.
Mimecast
Mimecast is a cloud-based email security and management tool that offers a comprehensive suite of anti-spam features. It is designed to protect businesses against email-borne threats such as spam, malware, and phishing attacks. The tool uses advanced filtering techniques such as content analysis, URL protection, and attachment sandboxing to detect and block spam emails before they reach the user's inbox. Additionally, Mimecast provides real-time updates and threat intelligence to ensure that it is always up to date with the latest threats. Mimecast also offers advanced features such as data leak prevention, email encryption, and email continuity, making it a comprehensive email security solution. With a user-friendly interface and customizable policies, Mimecast is suitable for businesses of all sizes and can be tailored to meet specific security and compliance needs.
Compared to SpamTitan:
- Filtering techniques: Both tools use advanced filtering techniques such as content analysis, URL protection, and attachment sandboxing to detect and block spam emails.
- Customizability: Both tools offer customizable policies and filters that allow organizations to tailor their anti-spam protection to their specific needs.
- Scalability: Both tools are scalable, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- Pricing: Mimecast's pricing model is generally considered to be more expensive than SpamTitan's, making it less accessible for smaller organizations.
- User interface: SpamTitan has a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and use, while Mimecast's interface may require some technical expertise to operate effectively.
Proofpoint
Proofpoint is a cloud-based email security and anti-spam tool that offers a range of advanced features to protect businesses against email-borne threats. It uses machine learning and advanced analytics to detect and block spam, phishing, and malware attacks in real-time, ensuring that users are protected from the latest threats. Additionally, Proofpoint offers email encryption, data loss prevention, and email continuity features, making it a comprehensive email security solution. With a user-friendly interface and customizable policies, Proofpoint is suitable for businesses of all sizes and can be tailored to meet specific security and compliance needs.
Compared to SpamTitan:
- Filtering techniques: Both tools use advanced filtering techniques such as content analysis, URL protection, and attachment sandboxing to detect and block spam emails.
- Real-time updates: Both tools provide real-time updates and threat intelligence to ensure that they are always up-to-date with the latest threats.
- Customizability: Both tools offer customizable policies and filters that allow organizations to tailor their anti-spam protection to their specific needs.
- Scalability: Both tools are scalable, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- Pricing: Proofpoint's pricing model is generally considered to be more expensive than SpamTitan's, making it less accessible for smaller organizations.
- User interface: SpamTitan has a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and use, while Proofpoint's interface may require some technical expertise to operate effectively.
VadeSecure
Vade Secure’s email security solutions are used to protect against advanced cybersecurity threats, including phishing and spam. The solution utilizes AI to provide email security and help to identify emerging threats and zero-day exploits. Vade Secure provides an extra layer of security, especially for Office 365 environments. The company is now venturing into the MSP market.
Compared to SpamTitan:
- Filtering techniques: SpamTitan uses RBLs but Vade Secure has no filtering at the SMTP level.
- Sandboxing: SpamTitan offers a sandbox to test out malicious emails, Vade Secure offers no sandbox facility.
- Granularity of settings: unlike SpamTitan, Vade Secure does not allow the setting of granular confidence levels by individual or role.
- MSP support: TitanHQ has worked with MSPs for years and SpamTitan is designed to be deployed and managed by an MSP if required. Vade Secure is a newcomer to the MSP market.
- Pricing: Vade Secure pricing is complex and expensive for MSPs. TitanHQ offers an attractive package for MSPs who wish to supply SpamTitan to clients.
Summary
Here are some reasons why a user might choose SpamTitan over similar anti-spam tools:
- Comprehensive filtering: SpamTitan uses advanced filtering techniques such as content analysis, URL protection, and attachment sandboxing to detect and block spam emails effectively.
- Zero day and emerging threat detection: SpamTitan uses AI-powered scanning to detect malicious content in incoming emails. SpamTitan opens incoming attachments in secure sandbox environment identify malware. If malicious content is identified, the email will be quarantined or deleted (depending on your company policy). If the email is found to be safe, it will be sent on to the recipient - all performed at lightning speed.
- Cost-effective: SpamTitan's pricing model is generally considered to be more affordable than other similar anti-spam tools, making it more accessible for smaller organizations.
- User-friendly interface: SpamTitan has a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and use, making it suitable for users with different levels of technical expertise.
- Customizability: SpamTitan offers customizable policies and filters that allow organizations to tailor their anti-spam protection to their specific needs.
- Scalability: SpamTitan is scalable, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- Excellent customer support: SpamTitan offers excellent customer support, with responsive and knowledgeable staff who can assist with any issues or questions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an anti-spam program, and why do I need it?
Anti-spamming software is designed to block unwanted or unsolicited emails, such as spam or phishing emails. It helps to protect your email inbox from spam emails and malicious attacks, reducing the risk of security breaches, data theft, and malware infections.
What is the secret of successful spam filtering on Office 365/M365?
Microsoft 365 includes a basic level of protection against malware and spam through Exchange Online Protection (EOP); however, tests have shown EOP is not very effective at blocking zero-day and advanced phishing threats. By layering a third-party spam filter software such as SpamTitan on top of Office 365, you will increase the spam, malware, and phishing detection rate to well above 99.9%.
How does SpamTitan provide protection against phishing?
SpamTitan checks each email for phishing-related keywords and embedded URLs are checked against 6 specialist blocklists of known spam and phishing sources and greylisting to identify new sources of phishing emails. DKIM, SPF, and DMARC tests identify email impersonation attacks, and outbound scanning is used to detect compromised email accounts.
Why is outbound scanning important?
Outbound scanning detects and prevents spam and phishing emails from being sent from your email accounts by malicious insiders and threat actors who have gained access to an email account. This allows email account compromises to be detected quickly, protects against data loss, and prevents your IP from being blocklisted.
How can I improve phishing and malware detection on Office 365?
To protect against sophisticated malware and phishing threats you will need to augment the Office 365 spam filter, as it only provides a basic level of protection. SpamTitan email security works seamlessly with Office 365 and adds advanced threat protection features such as sandboxing, greylisting, data leak prevention, and recipient verification, and includes inbuilt Bayesian auto-learning and heuristics.
How much does an advanced software spam filter cost?
An advanced spam filter should pay for itself by blocking more productivity-draining spam emails and threats that could easily result in a costly data breach. The cost will depend on the contract term, payment options, and number of users. To find out how little advanced spam filtering costs, use our cost calculator or call us for a no-obligation quote.
Can anti-spam tools block all spam emails?
No, it is impossible for any spam prevention tool to block all spam emails. However, advanced anti-spam tools like SpamTitan, Barracuda, and Mimecast can detect and block a high percentage of spam emails, reducing the number that reaches your inbox.
Can anti-spam software block legitimate emails?
It is possible for anti-spam software to mistakenly identify legitimate emails as spam and block them. However, SpamTitan avoids blocking legitimate emails by using a multi-layered approach to filtering, granular control over filtering policies, and end-user controls such as individual whitelists and blocklists. This ensures that only legitimate emails are allowed through, and that spam and malicious emails are filtered out without blocking important emails.
Does anti-spam software protect against viruses and malware?
Yes, many anti-spam solutions include virus and malware scanning as part of their features, helping to protect against email-borne threats such as ransomware, spyware, and trojans.
SpamTitan's advanced threat protection includes several layers of security to defend against evolving email-borne threats. The solution uses multiple antivirus engines to detect and block malware, ransomware, and other types of malicious content. Additionally, SpamTitan offers sandboxing and link protection to analyze and block advanced threats in real-time. The solution also features DMARC authentication to prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks. With these advanced security features, SpamTitan provides comprehensive protection against varied email-borne threats to keep organizations' networks and data safe.
Is it possible to try out anti-spam software before purchasing it?
Yes! TitanHQ offers a 14-day free trial of its SpamTitan anti-spam solution, allowing users to test the software's features and functionality before committing to a purchase. The trial includes full access to all features and support, as well as the ability to configure and test the solution in a live email environment.
Ready to Try Out SpamTitan from TitanHQ?
If your organization or MSP would like to leverage the best email anti-spam solutions, we invite you to try SpamTitan free of charge. You can begin with a free demo, allowing you to experience this powerful spam protection solution firsthand.
What do users say about SpamTitan?
Based on reviews and social media, users have expressed several positive things about SpamTitan. One of the most mentioned features is the tool's effectiveness in blocking spam emails. Users have noted that SpamTitan is highly accurate in detecting and filtering out unwanted emails, reducing the amount of spam that reaches their inboxes.
Another frequently mentioned aspect of SpamTitan is its user-friendly interface, which has been praised for being intuitive and easy to use. Many users have noted that they appreciate the tool's customizable policies and filters, which allow them to tailor their anti-spam protection to their specific needs.
In addition to the tool's effectiveness and ease of use, users have also highlighted the excellent customer support provided by SpamTitan. According to reviews and comments on social media, the company's support staff are responsive and knowledgeable, providing quick solutions to any issues or questions that users may have.


