Industry News
Our industry news section covers a broad range of news items of particular relevance to the cybersecurity industry and managed service providers (MSPs).
This section also included details of the latest white papers and research studies relating to malware, ransomware, phishing and data breaches. These articles provide some insight into the general state of cybersecurity, the industries currently most heavily targeted by cybercriminals, and figures and statistics for your own reports.
Hackers and scammers conduct massive spam campaigns designed to infect as many computers as possible. These attacks are random, using email addresses stolen in large data breaches such as the cyberattacks on LinkedIn, MySpace, Twitter and Yahoo. However, highly targeted attacks are increasing in frequency, with campaigns geared to specific industries. These industry-specific cyberattacks and spam and malware campaigns are detailed in this section, along with possible mitigations for reducing the risk of a successful attack.
This category is therefore of relevance to organizations in the education, healthcare, and financial services industries – the most common attacked industries according to recent security reports.
The articles contain information about current campaigns, spam email identifiers and details of the social engineering tactics used to fool end users and gain access to business networks. By following the advice in these articles, it may be possible to prevent similar attacks on your organization.
by titanadmin | Feb 8, 2017 | Email Scams, Industry News, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Software, Website Filtering
Ransomware attacks on British schools have soared in recent weeks. The problem has become so serious that the British National Fraud and Cyber Crime Reporting Center, also known as Action Fraud, has issued a new ransomware warning to British schools.
Ransomware has grown in popularity with cybercriminals over the past 2 years, with attacks on organizations around the world soaring in 2016. 2017 may only be a few weeks old, but ransomware attacks are continuing at the high levels seen in 2016. Security experts predict that 2017 will see even more cyberattacks on schools and other educational institutions. Ransomware the attack method of choice.
Ransomware is a form of malware that encrypts data on a compromised system. A wide range of file types are locked with powerful encryption and a ransom demand is issued. If payment is made, the attackers claim they will supply the key to unlock the encryption. Without the key – the sole copy is held by the attackers – data will remain locked forever.
Some forms of ransomware have been cracked and free decryptors made available, but they number in the few. The majority of ransomware variants have yet to be cracked. Recovery depends on payment of the ransom or the wiping of the attacked system and restoration of files from backups.
While a standard charge per encrypted device was the norm early last year, ransomware is now more sophisticated. The attackers are able to set their payment demand based on the types of files encrypted, the extent of the infection, and the perceived likelihood of the victim paying up. Ransomware attacks on British schools have seen ransom demands of an average of £8,000 issued.
Ransomware Attacks on British Schools are Targeted, Not Random
Many ransomware attacks are random – Spam emails are sent in the millions in the hope that some of them reach inboxes and are opened by employees. However, ransomware attacks on British schools have seen a different approach used. Recent attacks have been highly targeted.
Rather than send emails out en masse, the spate of recent ransomware attacks on British schools start with a phone call. In order to find their target, the attackers call the school and ask for the email address of the head teacher. The email address is required because sensitive information needs to be sent that should only be read by the head teacher. Information such as mental health assessment forms and teacher guidance forms.
An email is then crafted and sent to the head teacher; addressed to that individual by name. While there are many types of ransomware emails, a number of recent ransomware attacks on British schools involved an email that appears to have been sent by the Department of Education. Other cases have involved the impersonation of the Department of Work and Pensions and telecom providers.
In the text of the email the attacker explains that they have sent some information in an attached file which is important and needs to be read. The attached file, usually in compressed format such as .ZIP or .RAR, contains files that install ransomware if opened.
These ransomware downloaders may be JavaScript files, Word or Excel macros, or a host of other file types. In some cases, links are used instead of attachments. The links are masked so they appear to be official webpages; on the Department for Education website for example. In the case of links, they direct the recipient to a webpage containing an exploit kit or other form of file downloader. Just visiting that link could infect the user’s computer, mapped network drives, and portable storage devices.
How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks on British schools can be highly sophisticated, although risk can be effectively mitigated.
- Ensure all staff with computer access are made aware of the risk of ransomware attacks
- Provide cybersecurity training to all staff, including how to identify ransomware and phishing emails
- Never open attachments or visit links in emails sent from unknown senders
- Implement a spam filter to capture and quarantine malicious spam emails
- Use a web filtering solution to prevent staff members from visiting malicious links and from downloading ‘risky’ files
- Ensure all software is kept up to date and patches are applied promptly
- Keep all anti-virus and anti-malware solutions up to date, setting updates to occur automatically
- Restrict the use of administrator accounts – Only use accounts with high levels of privileges for specific tasks
It is also essential to ensure that backups of all data are made on a daily basis and backup devices are disconnected after backups have been performed. Data should ideally be backed up to the cloud and on a physical backup device. In the event of an attack, data can then be recovered without paying the ransom.
by titanadmin | May 20, 2016 | Email Scams, Industry News, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Advice, Spam News
According to a recent report on spam email from anti-virus software developer Kaspersky Lab, the decline in spam email over the past few years appears to have reversed, with the first quarter of 2016 seeing a major increase in malicious spam email volume.
Major Increase in Malicious Spam Email Volume Reported by Kaspersky Lab
Over the past few years there has been a decline in the number of spam emails, as cybercriminals have sought other ways to deliver malware and defraud computer users. In 2015, the volume of spam emails being sent fell to a 12-year low. Spam email volume fell below 50% for the first time since 2003.
In June 2015, the volume of spam emails dropped to 49.7% and in July 2015 the figures fell further still to 46.4%, according to anti-virus software developer Symantec. The decline was attributed to the taking down of major botnets responsible for sending spam emails in the billions.
Malicious spam email volume has remained fairly constant during 2015. Between 3 million and 6 million malicious spam emails were detected by Kaspersky Lab throughout 2015; however, toward the end of the year, malicious spam email volume increased. That trend has continued in 2016.
Kaspersky Lab figures show that spam email messages containing malicious attachments – malware, ransomware, malicious macros, and JavaScript – started to increase in December 2015. That rise has continued, and in March 2016 malicious spam email volume had risen to four times the level seen in 2015. In March, 2016, Kaspersky Lab detected 22,890,956 malicious spam emails. Spam email volume as a whole increased over the quarter, rising to an average of 56.92% for the first three months of 2016.
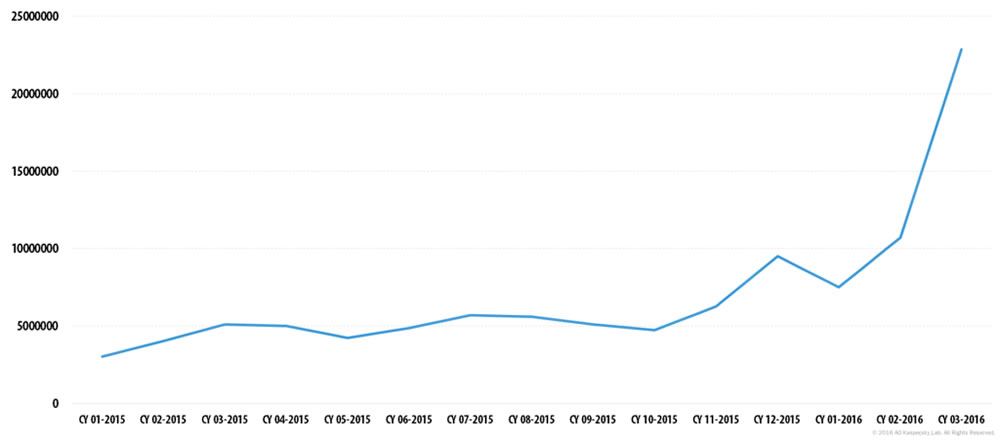
Image source: Kasperky Lab
Wide Range of Malicious Files Being Sent in Spam Email
While it was common for virus-loaded executable files to be sent as email attachments, these are now commonly caught by email filters and are marked as spam. However, spammers have been developing new methods of getting past traditional webmail spam filters. The spam emails intercepted by Kaspersky Lab now contained a wide variety of malicious files.
One of the most common methods now used by spammers is to send office documents infected with malicious macros. Microsoft Word files with the extension DOC and DOCX are commonly used, as are rich text format files RTF, Adobe PDF files, and Microsoft Excel spreadsheets with the extensions XLS and XLSX.
These file formats are commonly opened as many end users are less suspicious of office documents than they are about ZIP, RAR, and EXE files. Most office workers would know not to open a EXE file that was emailed to them by a stranger, yet an office document – a file format they use on a daily basis – is less likely to arouse suspicion.
Instead of the emails containing the actual malware, virus, or ransomware payload, they contain Trojan downloaders that download JS scripts. Those scripts then perform the final stage of infection and download the actual malware or ransomware. This method of attack is used to bypass anti-virus protections.
Web Filters and Email Spam Filters Should be Used to Reduce the Risk of a Malware Infection
There has been an increase in drive-by downloads in recent years as attackers have lured victims to websites containing exploit kits that probe for vulnerabilities in browsers and browser plugins. Visitors are redirected to these malicious websites when visiting compromised webpages, via malvertising, and malicious social media posts. While drive-by downloads are still a major threat, the use of web filters and anti-virus software browser add-ons are blocking these malware downloads and malicious websites.
Email is still a highly effective way of getting past security defenses and getting end users to install malware on their devices. Carefully crafted emails that include unique text increase the likelihood of the scammers getting users to open malicious attachments. Oftentimes, the messages include personal information about the recipient such as their name or address. This has helped the spammers to get the victims to take the desired action and run malicious macros and install malware.
It may be too early to tell whether spam email volume has only temporarily spiked or if there is a reversal in the decline of spam, but organizations and individuals should remain vigilant. The increase in malicious spam email volume should not be ignored.
Staff members should receive regular training on how to identify malicious email messages and phishing scams. It is also a wise precaution to use a robust spam filter such as SpamTitan. SpamTitan blocks 99.97% of malicious spam email messages, dramatically reducing the probability of malware, ransomware, adware, and spyware being installed.
by titanadmin | Apr 15, 2016 | Email Scams, Industry News, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam News
Over the past three years business email compromise scams have been conducted with increasing regularity. However, over the past year the number of business email compromise scams reported to the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) have increased dramatically.
Since January 2015, the FBI reports there has been a 270% increase in BEC attacks. FBI figures suggest the total losses from business email compromise scams since October 2013 has risen to $2.3 billion. Reports of successful BEC scams have been sent to the FBI from over 79 different countries around the world, which have affected more than 17,642 businesses.
Business email compromise scams involve the attacker gaining access to a corporate email account, such as that of the CEO, and requesting a bank transfer be made to their account. An email is sent from the CEO’s account to an accounts department employee, and all too often the transfer is made without question.
Unfortunately for U.S Businesses, BEC attacks are likely to increase as more cybercriminals get in on the act. Security experts have warned that the situation is likely to get a lot worse before it gets better. With the average fraudulent bank transfer between $25,000 and $75,000 and considerable potential to obtain much higher sums, criminals are more than willing to conduct the attacks.
A recent report from Dell SecureWorks indicates some hackers are selling their services on underground marketplaces and are offering access to corporate email accounts for just $250. Since cybercriminals could buy access to corporate email accounts, even relatively unskilled criminals could pull off a BEC scam and potentially have a million dollar+ payday. A number of large corporations have been fooled by these scams and have recorded losses of well over $1 million.
Business Email Compromise Scams Can Be Highly Convincing
BEC scams are convincing because even with security training, staff members tend to assume attacks will come from outside their organization. Employees are suspicious about emails that request the disclosure of login credentials, and a request to make a bank transfer that has not come from within an organization is likely to be immediately flagged as a scam.
However, when the CEO sends an email to a member of the accounts department requesting a bank transfer, many employees would not think to question the request. The person arranging the transfer would be unlikely to call the CEO to confirm payment. The transfer may go unnoticed for a number of days, by which time the funds would have been withdrawn from the attackers account and would be impossible to recover.
To conduct this type of attack the attacker would need to gain access to the email account of the CEO or an executive in the company who usually sends bank transfer requests to the accounts department. Once access has been gained, the attacker can read emails and learn the terminology typically used by that member of staff.
An email can then be written in the same language used by that individual. This ensures that the email does not rouse suspicions. Attackers research the transfer requests that are typically made and set the dollar amounts accordingly.
Since the account transfers are made to bank accounts outside the United States, the companies most frequently targeted are those that often make International payments. To the targeted accounts department employee, the request would seem perfectly normal.
How to Reduce the Risk of Employees Falling for BEC Scams
There are a number of ways that organizations can reduce the risk of employees falling for business email compromise scams. SpamTitan could not block a request sent from a compromised email account, but oftentimes attackers spoof email addresses. They purchase a domain that looks very similar to the targeted company, often transposing two letters. Oftentimes a domain is purchased replacing a letter “i” or an “L” with a “1”. If the email address of the sender is not carefully checked, this could well go unnoticed. SpamTitan can be configured to automatically block these spoofed email addresses to prevent these emails from being delivered.
To prevent employees from falling for business email compromise scams sent from compromised email accounts, policies and procedures should be introduced that require all account transfers to be verified by two individuals. Large transfers should also, where possible, be confirmed by some means other than email. A quick call to sender of the email for instance.
Organizations that choose to do nothing could regret failing to take precautions. Take the Austrian Airline parts company FACC for example. It reportedly lost approximately $55 million to such a scam.
by titanadmin | Mar 31, 2016 | Industry News, Internet Security, Network Security
The past two months have seen a number of healthcare organizations attacked by cybercriminals; however, the MedStar Health ransomware attack discovered on Monday this week must rank as one of the most severe.
The MedStar Health ransomware attack is the latest in a string of attacks on U.S. healthcare organizations, as hackers up the ante and go for much bigger targets where the potential rewards are greater. It would appear that the 10-hospital health system will not need to pay a ransom to regain access to its data, but for three days MedStar Health has been forced to work without access to some of its computer systems after they were shut down to prevent the spread of the infection.
MedStar Health Ransomware Attack Affects 10 Hospitals and More than 250 Outpatient Facilities
MedStar Health is a large U.S health system operating more than 250 outpatient facilities and ten hospitals in the Washington D.C., area. On Monday morning, a virus was discovered to have been installed. The infection triggered emergency IT procedures and rapid action taken to limit the spread of the virus. Three clinical information systems were shut down, including email and the electronic health record system used to record and view patient data.
Without access to email and patient data, services at the hospital were slowed although business continued as close to normal as possible. No facilities closed their door to patients. However, in the 48 hours since the virus was discovered, IT security teams have been working around the clock to bring systems back online. Yesterday, MedStar Health reported that systems were being brought back online with enhanced functionality added bit by bit.
MedStar Health has kept the media and patients notified of progress via social media. The health system reported that “The malicious malware attack has created many inconveniences and operational challenges for our patients and associates.”
While no information was initially released on the exact nature of the computer virus that was discovered to have infiltrated its systems, a number of sources indicate the malicious software was ransomware. It has since emerged that the MedStar Health ransomware attack involved a ransomware from the Samsam family. The ransomware is also known as MSIL and Samas. The attack occurred at the Union Memorial Hospital in Baltimore.
Some computer users were presented with a message demanding a ransom to unlock files. The Baltimore Sun reported that the MedStar Health ransomware attack saw attackers demand a ransom of 45 Bitcoin (approximately $18,500) to unlock all 18 computers that were infected, with an offer to unlock one machine for 3 Bitcoin (approximately $1233).
FBI Issued Warning About Samsam Ransomware on March 25
The FBI reached out to businesses for assistance dealing with the latest ransomware threat from Samsam. While many ransomware infections use email as the vector, Samsam is installed via a tool called JexBoss. JexBoss is used to discover a vulnerability that exists in JBOSS systems. This attack is not conducted using phishing or website exploit kits, instead it works by compromising servers and spreading the infection laterally.
The vulnerability exploited is in the default configuration of the Boss Management Console (JMX) which is used to control JBoss application servers. In its default state, JMX allows unsecured access from external parties and this is used to gain shell access to install the ransomware.
Once a web application server has been infected, the ransomware does not communicate with a command and control server, but will spread laterally and to infect Windows machines, hence the need to shut down systems. The MedStar Health ransomware attack could have been much more severe had rapid action not been taken.
This attack highlights just how important it is to ensure that all systems are patched and default software configurations are changed. Other attacks recently reported by healthcare organizations in the United States have involved Locky ransomware, which is spread via exploit kits on compromised websites and via email spam. Healthcare organizations can protect against those attacks by using web filtering and anti-spam solutions. However, it is also essential to train staff never to open email attachments from unknown sources.
by titanadmin | Jan 22, 2016 | Industry News, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Software
What was the best antivirus software solution for 2015 for the enterprise?
Protecting against the ever increasing number of cyberthreats is a full time job. The attack surface is now broader than ever before and hackers are developing increasingly sophisticated methods of obtaining data. The measures that must now be implemented to keep cyberattackers at bay have also increased in diversity and complexity.
Once of the core protections required by all organizations and individuals is an anti-virus software solution, and there is certainly no shortage of choice. But what was the best antivirus software solution for 2015?
The best AV software engines rated by AV-Comparatives
What AV engine detects and removes the most malware? What product offers the best real world protection? Which boasts the best file detection rates? These are all important considerations if you want to keep your organization protected. These and other factors were assessed over the course of the year by AV-comparatives.
AV-Comparatives is an independent testing lab based in Innsbruck, Austria. Each year the company publishes a report detailing the results of the AV tests the company conducted over the course of the year. The report is an excellent indicator of performance.
The company tested 21 of the top AV products on the market, subjecting each to a wide range of rigorous tests to determine the potential of each to protect users against malicious attacks.
The test results clearly show that not all antivirus products are the same. While all AV engines under test offered an acceptable level of performance, “acceptable” may not be good enough for enterprise installations.
The best antivirus software solution of 2015
AC-Comparatives rated performance and issued a number of awards to companies that excelled in specific areas of antivirus and antimalware protection. Gold, Silver and Bronze awards were awarded along with an overall best antivirus software solution for 2015 award.
Antivirus award categories:
- Real-world detection
- File detection
- False positives
- Overall performance
- Proactive protection
- Malware removal
Contenders for the ‘Best Antivirus Software Solution for 2015 Awards’
The Antivirus protects tested and considered for the awards were:
- Avast Free Antivirus
- AVG Internet Security
- Avira Antivirus Pro
- Baidu Antivirus
- Bitdefender Internet Security
- BullGuard Internet Security
- Emsisoft Anti-Malware
- eScan Internet Security Suite
- ESET Smart Security
- F-Secure Internet Security
- Fortinet FortiClient (with FortiGate)
- Kaspersky Internet Security
- Lavasoft Ad-Aware Free Antivirus+
- McAfee Internet Security
- Microsoft Windows Defender for Windows 10
- Panda Free Antivirus
- Quick Heal Total Security
- Sophos Endpoint Security and Control
- Tencent PC Manager
- ThreatTrack VIPRE Internet Security
- Trend Micro Internet Security
The Best Antivirus Software Solution for 2015 Award
After assessing all categories of anti-virus protection there were two AV products that excelled in all categories and received an Advanced+ rating: Bitdefender and Kaspersky Lab, with Kaspersky Lab bestowed the best antivirus software solution for 2015. Kaspersky Lab is one of the two AV engines at the core of SpamTitan anti-spam solutions.
The Russian antivirus company also received a Gold Award for “Real-World” protection, file detection, and malware removal, as well as a Silver Award for proactive (Heuristic/Behavioral) protection, and a Bronze Award for overall low system impact performance.
Cet article est disponible en anglais.
by titanadmin | Dec 16, 2015 | Industry News, Internet Security, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Software, Website Filtering
Following the recent news that Intel Security will be discontinuing McAfee SaaS Email Protection products, SpamTitan is preparing for 2016 when business customers start looking for a new email security vendor to ensure continued protection.
McAfee SaaS Email Protection to Come to an End
Intel Security, the new company name for McAfee, has taken the decision to exit the email security business. The company will be dropping McAfee SaaS Email Protection products and will be concentrating on other areas of business.
From January 11, 2016, McAfee SaaS Email Protection and Archiving and McAfee SaaS Endpoint will stop being sold by Intel Security. The news is not expected to trigger a mass exodus in early 2016, as Intel Security has announced that it will continue to provide support for the products for a further 3 years. Support for both McAfee SaaS Email Protection and Archiving and SaaS Endpoint will stop after January 11, 2019. However, many customers are expected to make the switch to a new email security provider in the new year.
SpamTitan Technologies Anti-Spam Solutions
SpamTitan Technologies offers a range of cost effective business email security appliances which keep networks protected from malware, malicious software, and email spam. Users benefit from dual AV engines from Bitdefender and Clam Anti-Virus, offering excellent protection from email spam, phishing emails, and inbox-swamping bulk mail.
SpamTitan is a highly effective anti-spam solution that was first launched as an image solution. Following an agreement with VMware, SpamTitan was developed into a virtual appliance. The range of anti-spam products has since been developed to include SpamTitan OnDemand in 2011 and SpamTitan Cloud in 2013. In August 2015, SpamTitan blocked 2,341 billion emails and has helped keep business networks free from malware and viruses.
SpamTitan was the first Anti-Spam Appliance to be awarded with two Virus Bulletin VBSPAM+ awards and has also received 22 consecutive VBSpam Virus Bulletin certifications. Additionally, SpamTitan was awarded the Best Anti-Spam Solution prize at the Computing Security Awards in 2012.
Companies in over 100 countries around the world have chosen SpamTitan as their anti-email spam partner. The email security appliance stops 99.98% of email spam from being delivered.
WebTitan Web Filtering Solutions from SpamTitan Technologies
WebTitan Gateway offers small to medium businesses a cost effective method of blocking malware and malicious websites, with highly granular controls allowing individual, group, and organization-wide privileges to be set. Delivered as a software appliance that can be seamlessly integrated into existing networks, it is an essential tool to protect all business users and allow the Internet to be viewed securely.
WebTitan Cloud is a cloud-based web filtering solution requiring no software installations. Create your own web usership policies and block malware-infected websites, objectionable websites, and restrict Internet access to work-related content with ease. Benefit from a comprehensive set of reporting tools which allow the browsing activity of every end user in the organization to be easily monitored.
WebTitan Wi-Fi has been developed for Wi-Fi providers and MSPs to allow easy control of Internet access. WebTitan Wi-Fi allows users to easily block objectionable content and malicious websites, with controls able to be applied by location. The cloud solution requires no software installations. All that is required to start protecting your business is a simple DNS redirect to WebTitan cloud servers.
WebTitan web filtering solutions blocked 7,414 malware-infected webpages in August 2015, and have helped keep businesses better protected from malicious website content, phishing campaigns, and drive-by malware downloads.
by titanadmin | Dec 10, 2015 | Email Scams, Industry News, Network Security, Phishing & Email Spam, Spam Software
In the United States, healthcare industry phishing campaigns have been responsible for exposing the protected health records of well over 90 million Americans over the course of the past 12 months. That’s over 28% of the population of the United States.
This week, another case of healthcare industry phishing has come to light with the announcement of Connecticut’s Middlesex Hospital data breach. The hospital discovered four of its employees responded to a phishing email, resulting in their email account logins being sent to a hacker’s command and control center. In this case the damage caused by the phishing attack was limited, and only 946 patients had their data exposed. Other healthcare organizations have not been nearly so lucky.
Largest ever healthcare industry phishing attack suffered in 2015
In February, Anthem Inc., the second largest health insurance company in the United States, discovered it had suffered the mother of all healthcare data breaches. Approximately 78.8 million health insurance subscriber records were obtained by criminals in the attack. The breach did not occur in February, but months previously, with the hackers being allowed plenty of time to exfiltrate data.
Another U.S. health insurance company discovered it too had been hacked just a couple of weeks later. Premera Blue Cross similarly found out that hackers had gained access to its systems many months previously and had potentially obtained the records of over 11 million insurance subscribers.
Both security breaches were highly sophisticated in nature, but were discovered to have their roots in healthcare industry phishing campaigns. Employees had responded to phishing emails which ultimately allowed hackers to gain access to huge volumes of highly confidential healthcare data.
In 2014, Community Health Systems suffered a data breach that exposed the PHI of 4.5 million individuals in what was then the second largest healthcare data breach reported. That data breach had its roots in a phishing campaign sent to its employees.
Healthcare industry phishing attacks occurring with alarming frequency
In just 12 months, many healthcare providers and health plans have suffered at the hands of phishers. Some of the healthcare industry phishing attacks have been summarized in the table below:
Successful U.S. Healthcare Industry Phishing Attacks in 2015
| Company |
Records Exposed |
| Anthem Inc. |
78,800,000 |
| Premera Blue Cross |
11,000,000 |
| CareFirst Blue Shield |
1,100,000 |
| Seton Healthcare |
39,000 |
| Saint Agnes HealthCare |
25,000 |
| Partners Healthcare |
3,300 |
| Middlesex Hospital |
946 |
| St. Vincent Medical Group |
760 |
Cybercriminals attracted by easy targets and big rewards
In the United States, healthcare organizations and their business associates are covered by legislation which requires robust protections to be put in place to keep computer networks secure and patient health data safeguarded from attack. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires administrative, technical, and physical controls to be used to keep the Protected Health Information (PHI) of patients secure at all times.
Even though the industry is heavily regulated, the industry lags behind others when it comes to data security. Hackers often see healthcare organizations as an easy target. Their networks are complex and difficult to protect, and IT security budgets are insufficient to ensure that all of the appropriate protections are put in place to keep data secure.
On top of that, healthcare providers and health insurers store an extraordinary volume of highly sensitive data on patients and subscribers. Those data are much more valuable to thieves than credit card numbers. Health data, Social Security numbers, and personal information can be used to commit identity theft, medical fraud, insurance fraud, credit card fraud, and tax fraud. One set of patient data can allow criminals to fraudulently obtain tens of thousands of dollars, and the data can typically be used for much longer than credit card numbers before fraud is detected.
It is therefore no surprise that healthcare providers are such a big target. There are potentially big rewards to be gained and little effort is required. Healthcare industry phishing is therefore rife, and spear phishing campaigns are now increasingly being used to get busy healthcare employees to reveal their login credentials. Many of those campaigns are proving to be successful.
Industry reports suggest that the healthcare industry in the United States does not have sufficient controls in place to prevent against phishing attacks. A KMPG study conducted earlier this year showed that 81% of U.S. healthcare organizations had suffered cyberattacks, botnet, and malware infections. Other research conducted by Raytheon/Websense suggested that the healthcare industry in the United States suffered 340% more data breaches than other industries.
Healthcare industry phishing emails are not always easy to identify
Just a few years ago, a phishing email could be identified from a mile away. They contained numerous spelling mistakes and grammatical errors. Nigerian 419 scams were commonly seen and easily spotted. Malicious email attachments were sent, yet they could be easily identified as they were rarely masked. It is easy to train staff never to open an executable file sent via email.
Today, it’s a different story. Healthcare industry phishing emails are not always easy to identify. Malicious emails are crafted with a high level of skill, spell checks are used, subjects are researched, as are the targets. Links are sent to phishing websites that cybercriminals have spent a lot of time, money, and resources developing. Even a trained eye can have trouble identifying a fake site from a real one. The threat landscape has changed considerably in just a few years.
Sometimes healthcare industry phishing emails are so convincing that many members of staff are fooled into responding. Franciscan Health System is a good example. In 2014, a phishing campaign was sent to the healthcare provider via email. The scam was straightforward. Workers were sent an email containing a link and a good reason to click it. They clicked through to a website which required them to enter their login credentials. 19 workers reportedly fell for the campaign and revealed their email account login names and passwords. Contained in their email accounts were patient data. As many as 12,000 patients were affected.
What can be done to reduce the risk of phishing attacks?
There are a number of controls and safeguards that can be implemented to reduce the risk of healthcare industry phishing campaigns being successful, and multi-layered defenses are key to reducing risk.
Conduct Regular Staff Training
All members of staff should be trained on email and internet security, and told how to identify phishing emails and phishing websites. They must be issued with a list of best practices, and their knowledge should be tested. The sending of dummy phishing emails is a good way to check to see if they have taken onboard the information provided in training sessions.
Use Powerful Anti-Virus and Anti-Malware Software
Separate anti-virus and anti-malware solutions should be used and virus/malware definitions updated automatically. Regular scans of the network and individual devices should be scheduled at times of low network activity.
Employ Spam Filtering Software
Spam filtering solutions are essential. One of the best ways of preventing end users from falling for phishing emails is to make sure they never receive them. Powerful anti-spam solutions will block and quarantine malicious email attachments and prevent phishing emails from being delivered to end users.
Implement Web Filtering Solutions
Not all phishing campaigns come via email. Social media websites are often used as an attack vector and malicious website adverts can direct users to phishing websites. Implementing a web filter to limit the types of websites that users are permitted to visit can significantly reduce the risk of users falling for a phishing campaign. Web filtering solutions will also block access to known phishing websites.

